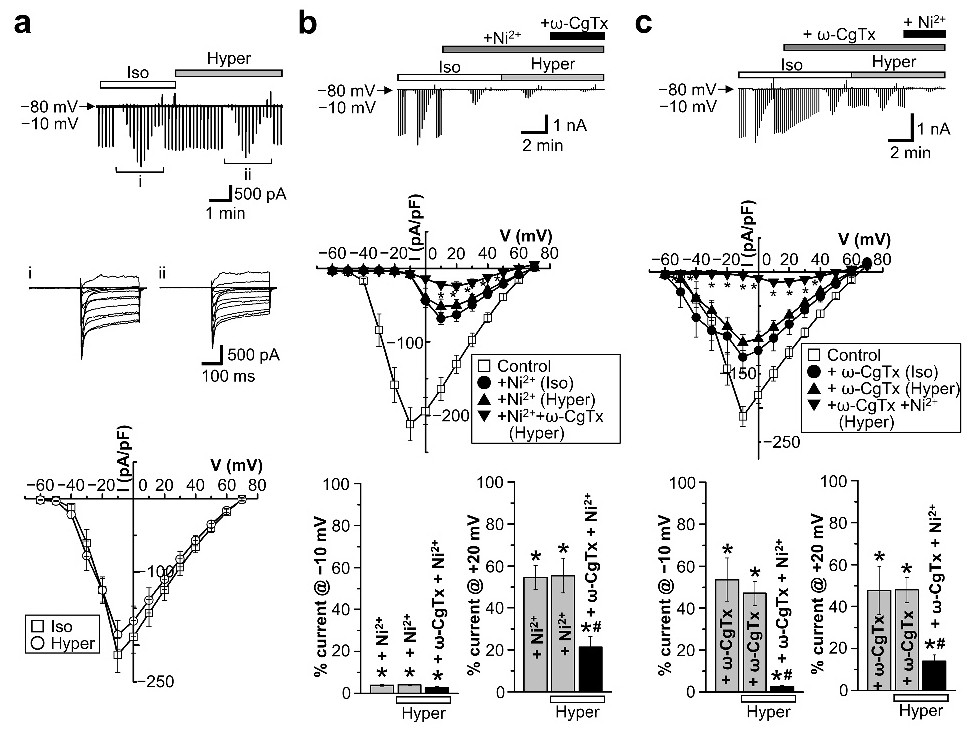
Fig. 5. The effects of Ni2+ and ω-CgTx on VGCC currents under isosmotic (Iso) or hyperosmotic (Hyper) conditions. (a) Representative record of currents before and after application of hyperosmotic bath solution (upper) and I-V relationships (bottom; n=14). Inset panels (middle) represent the expanded traces of current responses to step pulses from -60 to +70 mV applied at i and ii. (b) Representative record of currents (upper), I-V relationships (middle) and percent currents observed at −10 mV (bottom, left panel) and +20 mV (bottom, right panel) in the presence of Ni2+ (+Ni2+) under isosmotic and hyperosmotic conditions, and in the presence of Ni2+ plus ω-CgTx (+Ni2++ω-CgTx) under hyperosmotic conditions (bottom; n=6). *p<0.05 between +Ni2+ and +Ni2++ω-CgTx under hyperosmotic conditions in the middle panel and vs. Control in the bottom panel. #p<0.05 vs. +Ni2+ under hyperosmotic conditions in bottom panel. (c) Representative record of currents (upper), I-V relationships (middle) and percent currents observed at −10 mV (bottom, left panel) and +20 mV (bottom, right panel) in the presence of ω-CgTx (+ω-CgTx) under isosmotic and hyperosmotic conditions, and ω-CgTx plus Ni2+ (+ω-CgTx+Ni2+) under hyperosmotic conditions (bottom; n=8). *p<0.05 between +ω-CgTx and +ω-CgTx+Ni2+ under hyperosmotic conditions in the middle panel and vs. Control in the bottom panel. #p<0.05 vs. +ω-CgTx under hyperosmotic conditions in bottom panel.